Comprehensive automotive connection solution
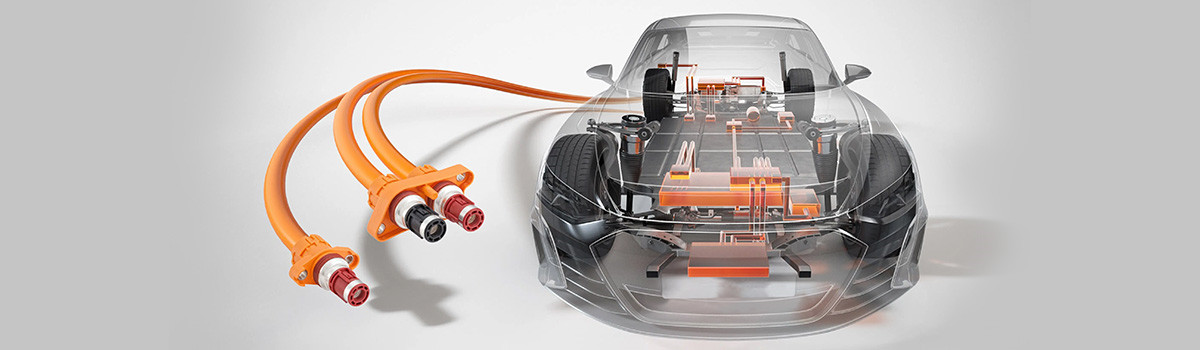
Cars today are equipped with electronic components that, in addition to the basic operations of moving, turning, and stopping, perform various other functions as well. Wiring harnesses are indispensable in controlling these electronic components, transmitting power and signals to every part of the vehicle. Comprising connectors, terminals, clamps, sheaths, and other elements surrounding a core of electrical wires, they are crucial components akin to the human body’s blood vessels and nerves.
A comprehensive automotive connection solution encompasses various technologies to facilitate reliable and secure communication within and around vehicles, enabling features like infotainment, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. These solutions leverage technologies like cellular connectivity, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth for various functionalities.
Wiring Harnesses for Automobiles that Connect You to the Cars
Automobiles are operated by a variety of electric controls such as being able to start the engine by pushing one button. Along with the increase in functions for automobiles, the number of electric devices installed is also increasing. The wiring harnesses play a role in connecting those devices and delivering electricity and signals through the entire car. The functions are similar to the blood vessels and nerves of a human body.
Here’s a more detailed look at what constitutes a comprehensive automotive connection solution:
1. Connectivity Technologies:
Cellular Connectivity:
4G LTE and 5G are crucial for connecting vehicles to the internet, enabling features like over-the-air (OTA) software updates, data logging, and remote diagnostics.
Wi-Fi:
Wi-Fi 6E is being increasingly used in vehicles for high-speed connections, particularly for in-vehicle infotainment and entertainment.
Bluetooth:
Bluetooth 5.3 is essential for connecting mobile phones, streaming audio, and enabling hands-free communication.
eSIMs:
eSIMs (embedded SIMs) provide a universal, secure, and flexible way to connect vehicles to cellular networks, simplifying manufacturing and logistics.
V2X Communication:
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, including V2V (vehicle-to-vehicle), V2I (vehicle-to-infrastructure), and V2N (vehicle-to-network), enables communication between vehicles, road infrastructure, and other network devices.
2. Functional Components:
Infotainment Systems:
These systems provide entertainment, navigation, and communication features, often utilizing cellular and Wi-Fi connectivity for apps, streaming, and online services.
ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems):
These systems, like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist, rely on connectivity for real-time data, maps, and traffic information.
Smart Car Access:
Features like digital car keys and NFC cards, powered by technologies like Bluetooth, NFC, and secure elements (SEs), enhance convenience and security.
Remote Management and Diagnostics:
Connected cars allow for remote monitoring of vehicle performance, diagnostics, and over-the-air software updates.
Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs):
SDVs prioritize software-based functionalities, enabling dynamic updates and customization of vehicle features through connected services.
3. Security Considerations:
Secure Subsystems:
Integrated secure subsystems, like NXP’s EdgeLock, protect connections and data from unauthorized access, ensuring secure communication and preventing cyberattacks.
Data Encryption:
Encryption is crucial for securing data transmitted between the vehicle and external systems, protecting sensitive information like personal data and vehicle telemetry.
Compliance with Regulations:
Solutions must adhere to relevant regulations, such as GDPR, for data privacy and security.
4. Key Players in the Automotive Connectivity Ecosystem:
OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers):
Car manufacturers like Hyundai, BMW, and Toyota are increasingly focused on connected vehicles and their associated services.
Aluminum Harnesses
Complying with the recent requirements of lower fuel consumption, safety, and riding comfort of the automobile, weight reduction of the wire harness (by 20-30 kg per vehicle) has become a more important issue. Instead of the copper wire which has been conventionally used, “high-strength aluminum alloy wire” is installed in the engine harness for the purpose of reducing weight and cost.
For the first time in the world, “high-strength aluminum alloy wires” are being used in engine harnesses, which have conventionally used copper wires. This development has resulted in harnesses offering about twice the strength of standard aluminum while maintaining their bending properties, all at a lower cost.
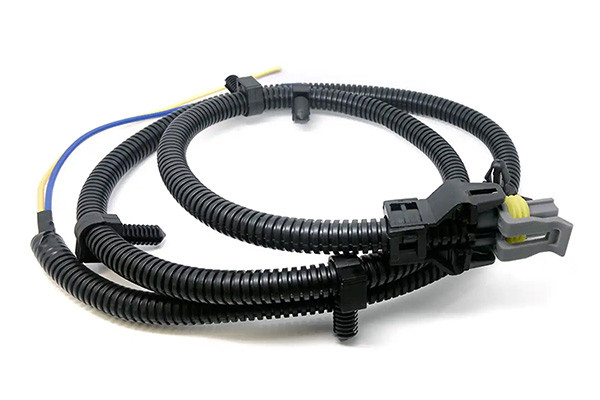

EPB* Harness Integrated with Wheel Speed Sensor
We have succeeded in developing the world’s first integrated wheel speed sensor and EPB harness, achieving reductions in both weight and cost. *EPB:Electric Parking Brake.
This product is an integration of a wheel velocity sensor and a harness for the EPB (Electric Parking Brake). Gvtong Wiring Systems was the first in the world to reduce the weight of the product and cut manufacturing costs, by integrating the wheel speed sensor to the harness for the EPB.
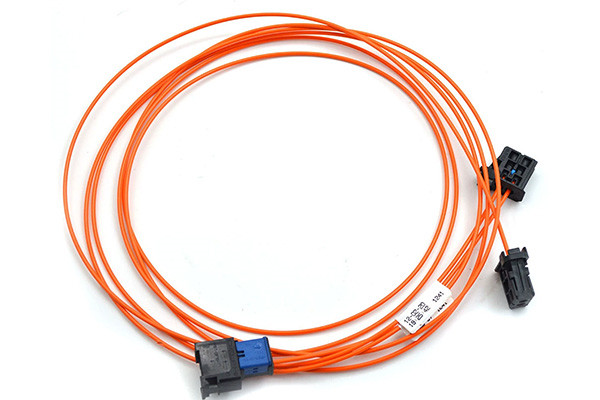
Optical Harnesses
These harnesses instantly transmit large amounts of data used in monitoring conditions around vehicles without being affected by electromagnetic noise.
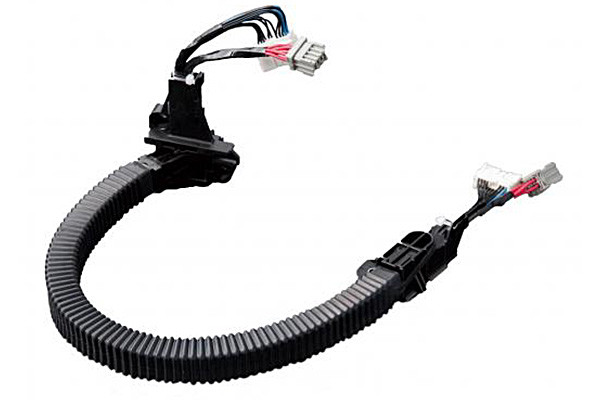


Wiring Harnesses for Sliding Doors
These convey electric power and signals to electrical components within sliding doors, regardless of whether the door is open, closed, or in operation. This allows opening and closing of the door to be automated.
Employed for the slide door of minivans, conveying electricity (power supply, signal) to electrical components installed in the door either in closed or opened state.
Properties
*Stable movement track (always moves on the same tracks)
*Fits inside the small space inside the door
*Prevents extraneous noise
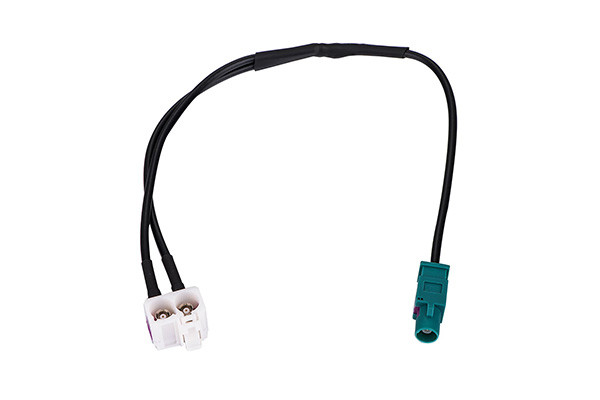
Antenna Harnesses
These connect the antenna to the receiver, conveying radio, TV, telephone, GPS, and other signals received by the antenna.

